The art pipeline is something often underlooked by indie developers. You may think that you don’t need one because you don’t have 3000 3D models with different textures, materials, etc.
It may be true if you only have a small amount of images, sounds and music. But there are some cases when it’s very important to have a good pipeline, and Reckless Squad is one of those.
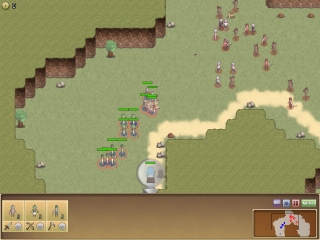
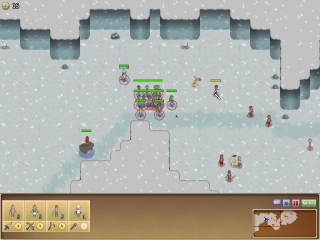
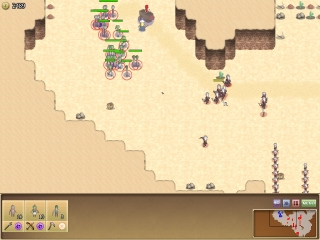
For the prototype of Reckless Squad, we used 2D sprites for the units:

They weren’t animated. I knew I needed 8 directions, at least 3 frames for walk animation, and a bunch of other animations like using a sword, a bow, or dying.
The amount of work was just astounding, and I knew I couldn’t do it alone. Worst, I’m not even an artist to begin with.
So I had to find a solution and use my abilities as a programmer to produce the needed content. Quickly it was clear that 3D was the way to go.
However, we didn’t want the game to be in 3D. It was a huge amount of work as it is in 2D, no need to add more complexity. So we used pre-rendered 3D graphics, like Diablo or Age of Empires.
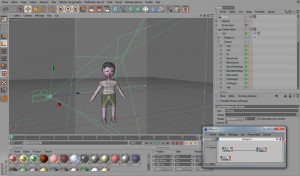
I used Cinema4D as a 3D package
To do it I started by modeling a base mesh with rough edges. Then I added Hyper NURBS to subdivide the mesh and make it look more organic.
I wanted to keep the look and feel of the 2D sprites, and I knew the final images wouldn’t be larger than 48×48 pixels. So I used really simple shapes, with few to no details and plain colors as textures.
Speaking of textures, I used palettes. If you played a NES or SNES RPG before, you may remember all the similar monsters with just different colors. It was because the developers used the same image with a different palette (to save memory). I used the same technique for Reckless Squad: I unwrapped the UV once, and then only changed the colors in the palette to make them match the unit.

The next step was rigging, no magic here: I just added bones and painted vertex weights. What’s interesting is how I used little scripts to attach props to the bones, because different colors would never be enough to differentiate the units.
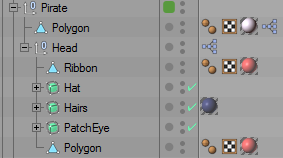
When the system to customize the base mesh was ready, it was time to add animations to it.
I first listed all the needed frames:
- 1 idle
- 3 walking
- 3 using a sword/staff
- 3 using a bow
- 3 dying
- 1 standing victorious
It’s 14 frames, for just one direction, meaning 112 for an entire sprite sheet.
I made the timeline 112 frames long, and started making poses using the previously created rig. Once I finished a direction, I copy/pasted it 7 times and rotated the model to face new directions.
It was time to setup the rendering. I decided to use global illumination to shade the models because I didn’t wanted to make the light come from just one direction, it wouldn’t feel very natural. With global illumination, the light seems to come from everywhere and makes the shape stand out. The downside was that the time to render a sprite would be quite long…
I configured the rendering so that it will save each frame to two bitmap files: one for the diffuse color and one for the alpha mask. It was the more automatic setup I could come up with.

So I basically had 224 bitmap files on my hard disk, and I needed to combine them into a sprite sheet usable by the game.
And I needed to make it automatic as well. So I wrote a little script in C# for that. The program create a blank texture sheet and then load the diffuse color and the alpha mask files for each frame and combine them before placing them on the sheet.
When finished, it saves the final sheet to a new PNG file, with transparency.

A finished sprite sheet
I’m glad I took the time to setup a real art pipeline as automated as possible, because I ended up with 46 sprite sheets.
5 152 frames in total. It would really have been impossible for me to do them by hand in a pixel art fashion.
However, we did have some concerns with the graphics, mainly all the units share the same silhouette. Using very different and instantly recognizable silhouettes make the game easier to play and visually nicer. Just look at Team Fortress 2 and the amazing work done by Valve to give each class a unique silhouette.
But I still know it would have been impossible to make them all by hand. Using morphing could be a solution, and it would be interesting to make some researches in this direction next time.











Newsletter: